Longyearbyen, the main settlement in the Svalbard archipelago, is located at 78°N in the European Arctic. Its climate is generally warmer than other locations at similar latitudes, due mainly to the influence of relatively warm Atlantic water in the surrounding waters. This water originates from the Gulf Stream. However, the average annual temperature in Svalbard still typically remains below 0°C in.
Svalbard has an Arctic climate, but it is relatively mild and wet compared to other high Arctic regions. This is largely due to the influence of the West Spitsbergen Current, the northernmost branch of the Gulf Stream, which transports warm Atlantic water northward into the Arctic. The average annual temperature between 1971 and 2000 was -8.7°C, but in recent decades temperatures have risen by 3 to 5°C. Svalbard is therefore warming much faster than the global average. Temperatures have risen even more in winter. As a result, many fjords along the west coast of Svalbard are largely ice-free for most of the year, even during winter.
Svalbard lies between cold Arctic air from the north and milder maritime air from the south, which leads to frequent storms, especially in winter. The region is dominated by northeasterly winds, but storm passages and mountains and fjords create variations.
Precipitation varies throughout Svalbard. Between 1971 and 2000, annual rainfall and snowfall ranged from 196 mm at Svalbard Airport to 581 mm at Barentsburg. However, snow and strong winds create uncertainties in these data. As a result of climate change, heavy winter precipitation has become more common in recent decades. Svalbard has the warmest permafrost this far north in the Arctic. At a depth of 10-20 m, permafrost temperatures range from -2.5°C along the coast to -5°C further inland. The permafrost has warmed considerably in recent years. [1]
To illustrate local variability in weather in Svalbard, we show example weather data from Longyeardalen August 2024 – August 2025.
([1] I. Hanssen-Bauer, et al. Climate in Svalbard 2100. The Norwegian Centre for Climate Services (NCCS), 2019.)
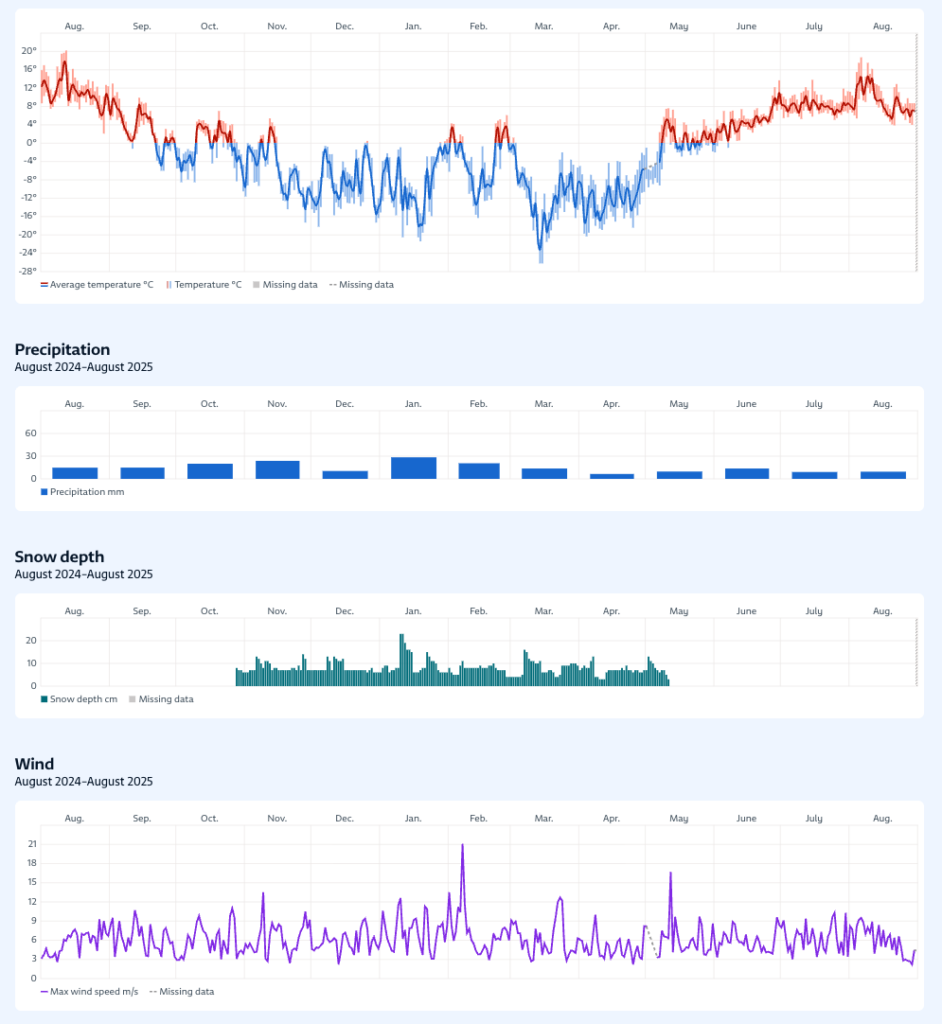
During the time period August 2024 – August 2025, the Longyeardalen central weather station recorded temperature of between −26.2°C (14 March) and +20.2°C (12 Aug.). The wettest day measured was 8 Feb. with 10.3mm precipitation. The highest wind speed was recorded at 21.1 m/s on 7 Feb. and the maximum snow depth was 23.0 cm.
The weather station is operated in a collaboration between MET Norway and UNIS and the figure is obtained from www.yr.no.

